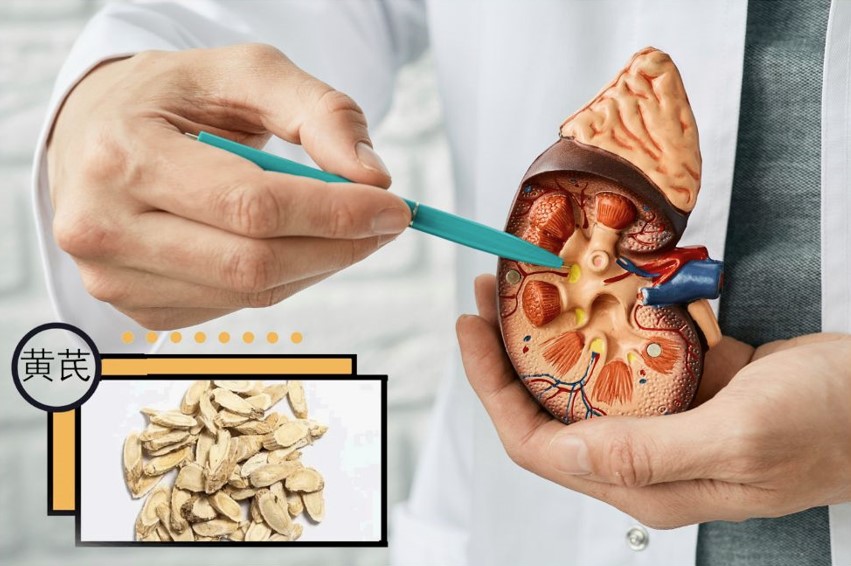
黄芪(Astragalus membranaceus,AM),是个常用的中药,黄芪被广泛用于治疗肾病综合症。肾病综合症的特征包括液体过载、外周水肿和蛋白尿等症状,是一种复杂的肾脏疾病。本研究评估了黄芪的免疫调节功能、在肾小球病理中的作用机制,以及含有黄芪的中药方剂与西药治疗相比的疗效和安全性。本研究的总结为:
- 作用机制:黄芪的可能通过以下几种机制发挥其作用:
-
- 免疫调节:黄芪调节免疫反应,可能通过减少炎症,增强保肾。
- 抗炎作用:黄芪能影响与炎症相关的关键细胞因子,如IL-1、IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α,从而减缓炎症对肾脏造成的损伤。
- 保护肾脏:黄芪能减少蛋白尿和高脂血症以显示它的保肾功能。
- 临床研究证据:对比含黄芪的中药方剂与标准西药治疗的随机对照试验(RCT)的综合评估得出以下结论:
- 生化改善:黄芪补充剂与生化标志物显著改善相关,包括蛋白尿的减少、高脂血症的减轻和血清白蛋白水平的升高。
- 肾功能:将黄芪添加到标准西药治疗中通常能保持或改善肾功能。
- 缓解率:接受含黄芪中药方剂的患者比单独接受标准西药治疗的患者表现出更高的缓解率。
- 炎症标志物:黄芪治疗组相比仅接受类固醇治疗的组,炎症细胞因子(IL-1、IL-6、IL-8、TNF-α)显著减少。
- 复发率降低:一些研究表明,接受黄芪治疗的患者复发率低于对照组。
- 安全性:黄芪通常耐受良好,与标准西药治疗相比,副作用或不良事件的发生没有显著差异。研究中使用的剂量范围为每日9到30克,符合《中国药典》的推荐范围。
关于黄芪与免疫抑制药物之间潜在相互作用的担忧已有注意。体外研究结果不一,且中药方剂的复杂性(通常包含多种草药)增加了隔离特定相互作用的挑战。然而,监测环孢素和他克莫司等免疫抑制药物的药物水平,有助于管理药物暴露潜在问题。
总之,现有证据支持黄芪作为原发性肾病综合症管理的辅助治疗。尽管所评审的RCT的Jadad评分普遍较低,表明需要进行更高质量的研究,但一致的积极结果表明,黄芪可能在不显著增加不良反应的情况下,改善缓解率和疾病标志物。需要进一步的严格研究,以更好地理解黄芪在肾病综合症管理中的长期效果和最佳使用方法。
References
- Block KI, Mead MN. Immune system effects of echinacea, ginseng, and astragalus: A review. Integrative Cancer Therapies. 2003, 2(3), 247-267.
- 曹广海, 魏磊, 田明, 等. 防己黄芪汤合越婢汤加减联合西药治疗小儿肾病综合征的临床效果观察. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志.2020,21(12):1064-1066.
- 陈静, 陈师群. 黄芪颗粒预防儿童肾病综合征感染的临床观察. 中国中西医结合杂志,2008,28(5):467-469.
- Chen Y, Deng Y, Ni Z, et.al. Efficacy and safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Shenqi Particle) for patients with Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy: A multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2013, 62(6), 1068–1076.
- Chen Z, Liu L, Gao C, et.al. Astragali Radix (Huangqi): A promising edible immunomodulatory herbal medicine. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2020:112895.
- Chu DT, Wong WL, Mavligit GM. Immunotherapy with Chinese medicinal herbs. I. Immune restoration of local xenogeneic graft-versus-host reaction in cancer patients by fractionated Astragalus membranaceus in vitro. Journal of clinical & laboratory immunology. 1988,25(3),119–123.
- Chu D T, Wong W.L, Mavligit GM. Immunotherapy with Chinese medicinal herbs. II. Reversal of cyclophosphamide-induced immune suppression by administration of fractionated Astragalus membranaceus in vivo. Journal of clinical & laboratory immunology. 1988,25(3):125–129.
- Cosyns JP. Aristolochic acid and ‘Chinese herbs nephropathy’: a review of the evidence to date. Drug Safety. 2003,26(1):33–48.
- 范德墉, 马基康. 环磷酰胺冲击疗法联合参芪地黄汤治疗成人难治性肾病综合征的临床研究.中华中医药学刊. 2014,32(2):435-437.
- Feng M, Yuan W, Zhang R, et.al. Chinese herbal medicine Huangqi type formulations for nephrotic syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2013(6)
- Gallagher MP, Kelly PJ, Jardine M, et.al. Long-term cancer risk of immunosuppressive regimens after kidney transplantation. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2010,21(5):852–858.
- Giorgi A. (2019, January 9). About Immunosuppressant Drugs. Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/immunosuppressant-drugs. [Accessed: 4 June 2019]
- Gong A, Duan R, Wang HY, et.al. Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Properties and Value of Astragali Radix. Medicines (Basel, Switzerland). 2018,5(2):46.
- 黄芳. 防己黄芪汤联合泼尼松治疗肾病综合征临床观察. 光明中医. 2020,35(13):2060-2062.
- 黄健光. 中西医结合治疗小儿难治性肾病的临床分析. 蛇志. 2010,22(3):227-228.
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et.al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Controlled Clinical Trials. 1996,17(1):1–12.
- 康国贵. 黄芪颗粒对儿童单纯性肾病综合征继发感染预防的初步探讨. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志. 2005,6(12):718-719.
- Kelepouris E, Rovin BH. 2021. Overview of heavy proteinuria and the nephrotic syndrome. In Richard J Glassock, Albert Q Lam (Ed), UpToDate (Accessed on 17 July 2021).
- Lau C, Mooiman KD, Maas-Bakker RF, et.al. Effect of Chinese herbs on CYP3A4 activity and expression in vitro. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2013,149(2):543–549.
- 雷帅兵. 他克莫司联合黄芪赤风汤治疗老年特发性膜性肾病. 河南中医研究. 2020,29(3):476-477.
- Li J, Liu, Z, Chen R, et.al. The quality of reports of randomized clinical trials on traditional Chinese Medicine treatments: A systematic review of articles indexed in the China National Knowledge Infrastructure database from 2005 to 2012. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2014,14(1):362.
- 李士旭. 加味防己黄芪汤联合醋酸泼尼松片治疗肾病综合征对肾功能及炎症指标的影响. 实用中医药杂志. 2020,36(5):641-642.
- 李晓妍, 王华. 玉屏风颗粒对儿童肾病综合征患者免疫功能的影响. 河南医学研究. 2016,25(11):1927-1929.
- 刘天媚, 陈元史, 邓行行. 加味防己黄芪汤联合激素治疗对小儿原发性肾病综合征肾功能、血脂及血凝状态的影响. 世界中医药. 2019,14(4):950-953.
- Liu W, Liu G, Liu J. Effects of Astragaloside IV on the pharmacokinetics of omeprazole in rats. Pharmaceutical Biology. 2019,57(1):449–452.
- 马娜, 王建萍, 刘熙如. 加味防己黄芪汤治疗原发性肾病综合征50例. 河南中医. 2019,39(2):180-183.
- McCulloch M, See C, Shu X, et.al. Astragalus-Based Chinese herbs and Platinum-Based chemotherapy for Advanced Non–Small-Cell lung Cancer: Meta-analysis of randomized trials. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2006,24(3):419–430.
- Pao LH, Hu O YP, Fan HY, et.al. Herb-Drug interaction of 50 Chinese herbal medicines on CYP3A4 activity in vitro and in vivo. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 2012,40(01):57–73.
- 邱建军, 解冰. 清热解毒活血汤联合西药治疗难治性肾病综合征疗效观察. 吉林中医药.2007,27(10):16-17.
- Roberts MB, Fishman JA. Immunosuppressive Agents and Infectious Risk in Transplantation: Managing the “Net State of Immunosuppression”. Clin Infect Dis. 2021,73(7):e1302-e1317.
- Song J, Meng L, Li S, et.al. A combination of Chinese herbs, Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus and Angelica sinensis, improved renal microvascular insufficiency in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Vascular Pharmacology. 2009, 50(5-6):185–193.
- Su G, Iwagami M, Qin X, et.al. Kidney disease and mortality in patients with respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Kidney Journal. 2020,14(2):602–611.
- 苏励, 茅建春, 顾军花. 环磷酰胺联合大剂量黄芪注射液静脉滴注治疗狼疮性肾炎. 中西医结合学报. 2007,5(3):272-275.
- 孙宏, 杨曦. 加味防己黄芪汤治疗原发性肾病综合征临床观察. 光明中医. 2020,35(9):1340-1343.
- Sun V, Hersh EM, Talpaz M, et.al. Immune restoration and/or augmentation of local graft versus host reaction by traditional Chinese medicinal herbs. Cancer. 2006,52(1):70–73.
- 王海燕, 李惊子, 潘缉圣, 等. 中药黄芪当归合剂对肾病综合征肾损伤的保护作用及对代谢紊乱的影响. 北京大学学报(医学版). 2002,34(5):542-552.
- 王群林. 参芪地黄汤加减方联合他克莫司及小剂量激素治疗特发性膜性肾病的临床研究. 山东中医药大学硕士学位论文. 2016.
- 王元真, 赵汉儒, 林丽娟.黄芪当归合剂联合他克莫司对难治性肾病综合征患者免疫功能及肾功能的影响. 上海中医药杂志. 2019,53(6): 58-60.
- 王召伦.中西医结合治疗难治性肾病综合征的疗效观察. 亚太传统医药. 2010,6(2):40-41.
- 谢晓玲, 彭芸. 黄芪辅助治疗肾病综合征及预防反复感染疗效观察. 湖北中医杂志. 2010,32(5):9-10.
- 杨爱华, 孙晔. 黄芪配合泼尼松治疗原发性肾病综合征35例疗效分析.农垦医学. 2000,22(6):395-396.
- 杨协清.黄芪颗粒联合激素对原发性肾病综合征患儿血尿白介素的影响. 中国药师. 2013,16(8):1202-1204.
- 于力,卓美瑛,杨小苏,等. 黄芪注射液对肾病综合征细胞因子及其基因表达的影响. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志. 2001,2(9):523-525.
- Yu SY, OuYang HT, Yang JY, et.al. Subchronic toxicity studies of Radix Astragali extract in rats and dogs. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2007,110(2):352–355.
- 于跃. 参芪汤联合他克莫司治疗脾肾两虚型Ⅰ-Ⅱ期膜性肾病临床观察. 黑龙江中医药科学院硕士学位论文. 2015.
- 袁慧中, 谢放, 张春天. 黄芪与红枣在常复发型原发性系膜增生性肾炎肾病综合征激素减量过程中的应用. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志. 2004,5(7):413-414.
- Zhang K, Pugliese M, Pugliese A, et.al. Biological active ingredients of traditional Chinese herb Astragalus membranaceus on treatment of diabetes: a systematic review. Mini reviews in medicinal chemistry. 2015,15(4):315–329.
- Zhang Y, Huang L, Bi H, et.al. Study of the upregulation of the activity of cytochrome P450 3A isoforms by astragalus injection and astragalus granules in rats and in cells. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. 2012,38(2):105–113.
- Zhang Y, Sun S, Li S, et.al. Laws of TCM Syndromes of Refractory Nephrotic Syndrome and Characteristics of Chinese Medicinal Herbs Used: A Data Mining Based on Literature. Journal of Liaoning University of TCM. 2018,20(3):149-153.
- 赵翠, 贾利敏, 陈保春,王自强,房晓芳,魏迪,杜书同. 健脾益肾活血中药方治疗不典型膜性肾病的疗效观察及血栓弹力图变化.中国中医药科技. 2020,27(1):62-64.
- 赵辉. 黄芪地黄汤联合西药治疗难治性肾病综合征的效果观察. 中国疗养医学. 2018,27(12):1310-1312.
- 赵学兰, 林松娟, 肖青. 黄芪当归合剂配合西医治疗原发性肾病综合征. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志. 2001,2(1):23-25..
- Zou C, Su G, Wu Y, et.al. Astragalus in the prevention of upper respiratory tract infection in children with nephrotic syndrome: Evidence-based clinical practice. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013:1–10.